2 minutes
ECOM7121 Digital and Network Economics
Network Effects
- function
- one way to create competitive “moats” in the digital world
- categories
- direct network effects -> more searchers, better search
- indirect network effects -> more apps, more smartphone buyers
- cross-network effects -> more searchers, more advertisers (e.g., keywords monetize the “long tail” of advertising)
- social network effects -> social influence & local effects
- demand-side network effects -> exclusivity, dynamic pricing, limited access, keyword auctions
- example

- power laws
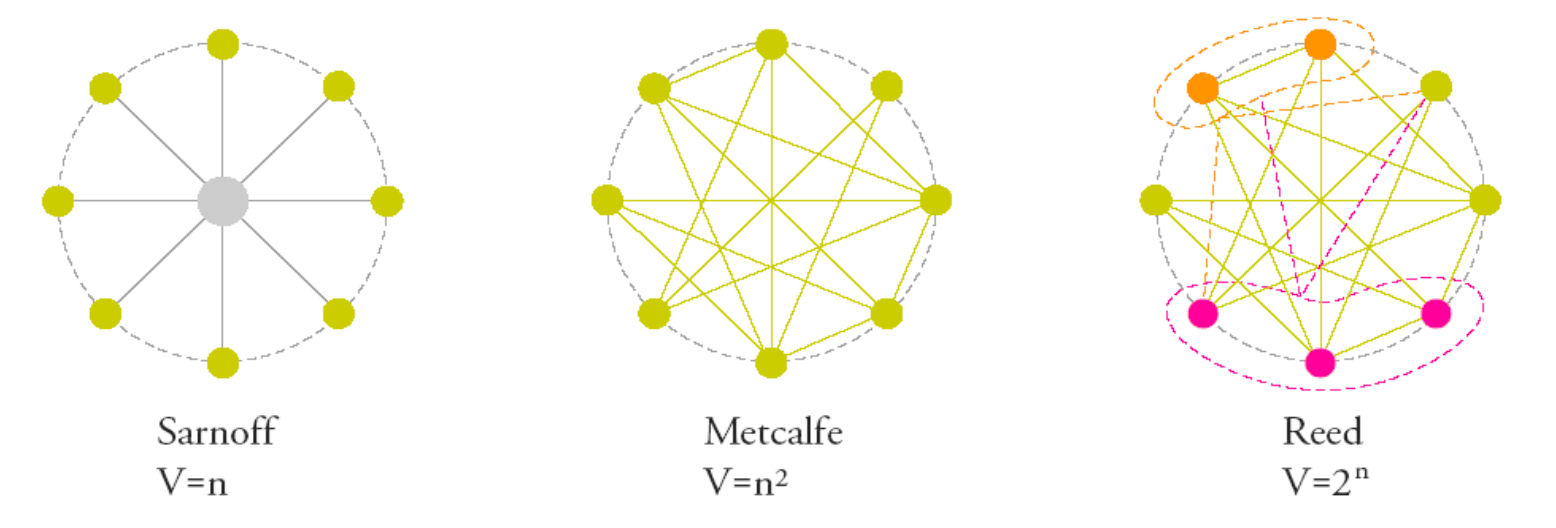
- n is the number of network links
- tips: remember to multiply each link’s worth
PlentyofFish
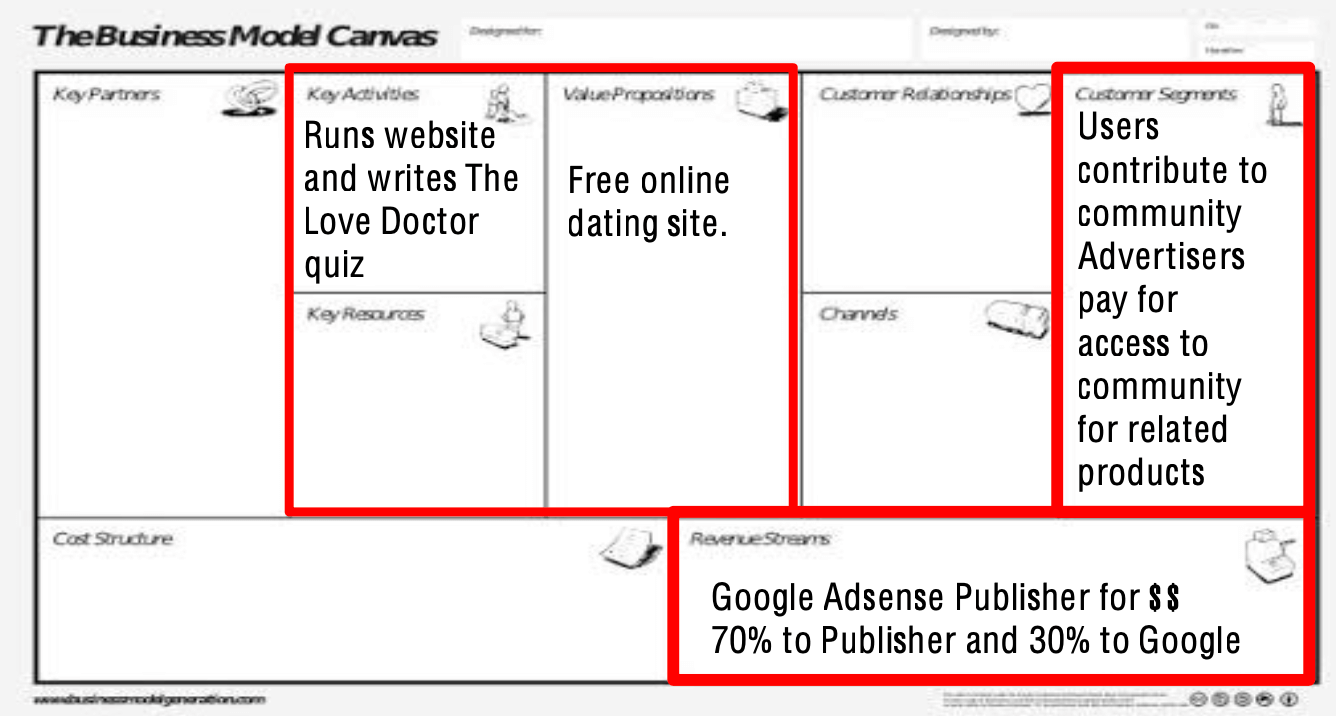
- business model analysis
- itself
- free online dating site
- runs website and writes the love doctor quiz
- adsense
- Google Adsense Publisher Blogging for money
- volunteers contribute to community
- advertisers pay for access to community for related products
- ad-based revenue
- PPC and keyword pricing
- 70% to publisher and 30% to Google
- money/week or money/year, low fixed costs
- itself
- canvas
- social media monetization
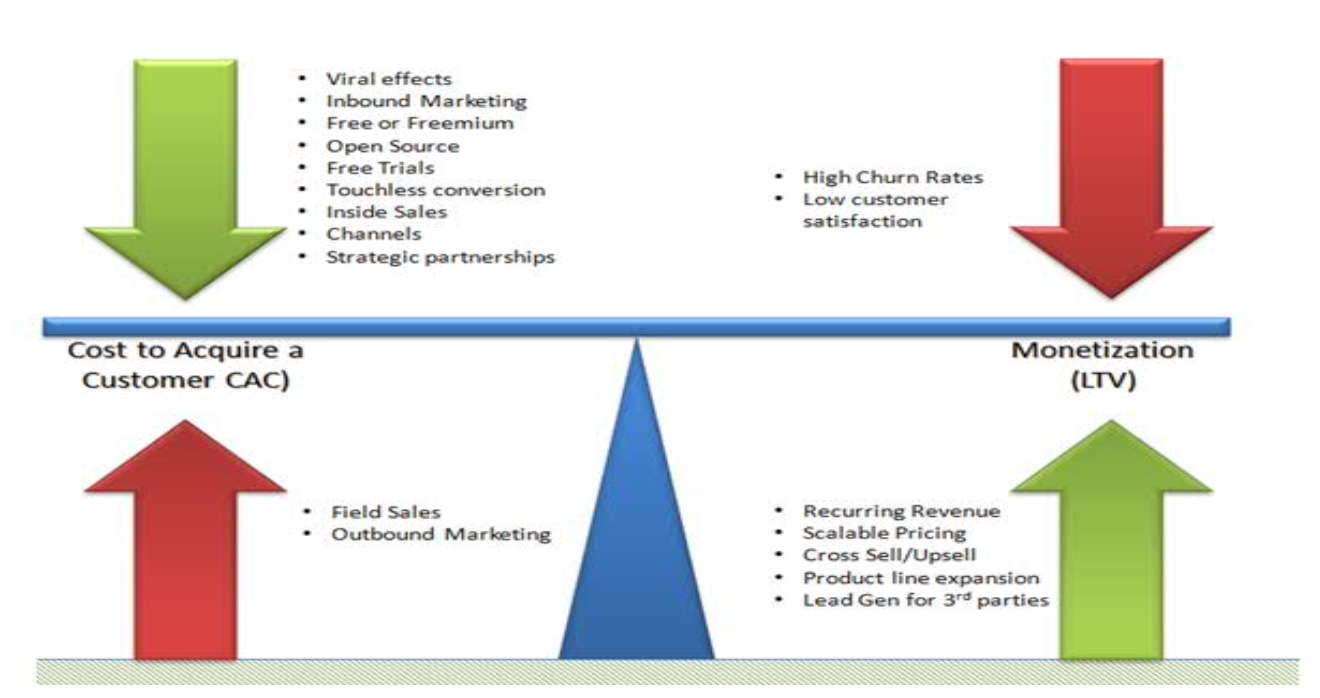
- RPU - average revenue per user
- CAC - cost to acquire a customer
- LTV - lifetime value of user
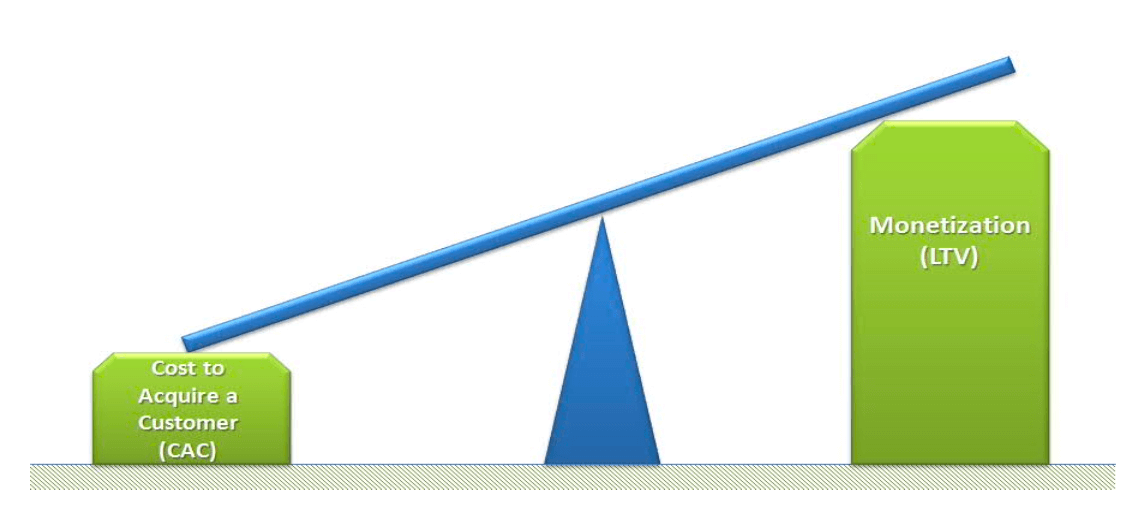
- what can drive the balance
- summary
- PlentyofFish and “free online dating” changes the customer relationship to a “community platform”— with users contributing time and self-policing
- PlentyofFish makes money on a free dating service through Google’s Adsense program
- PlentyofFish is very profitable, and Google Adsense pays Marcus Fried $1M a month & costs are very low
- we can calculate RPU—revenue per user—on a free or freemium service by taking $1M divided by monthly active users in the community
- Lui Mama, the livestreaming Chinese pig farmer is also very profitable, but is “gift” not ad-supported
Updating Dating
- some examples - profile, matching, monetization
- Coffee meets Bagel - Facebook, bagels/beans
- OKCupid - questionnaire, suggestions
- Jiayuan – user data, proof of employment
- Dating Ring - human & algorithmic matches
- Hurry Date - 4 minute exchanges
- monetization strategies
- user engagement vs high quality/seriousness
- pros and cons of
- subscription
- pay per message
- summary
- major shift in past 20 years to online dating
- younger adults have newer experience and expectations of mobile dating
- Tinder gamified the industry by fun “swiping”
- online dating is big in China
- dating apps address key “market failure” issues and monetization differently
Additional Reading
ecom7121 dynamic digital capabilities digital and network economics network effects
367 Words
2020-11-17 11:10