3 minutes
ECOM7121 The On-Demand Economy
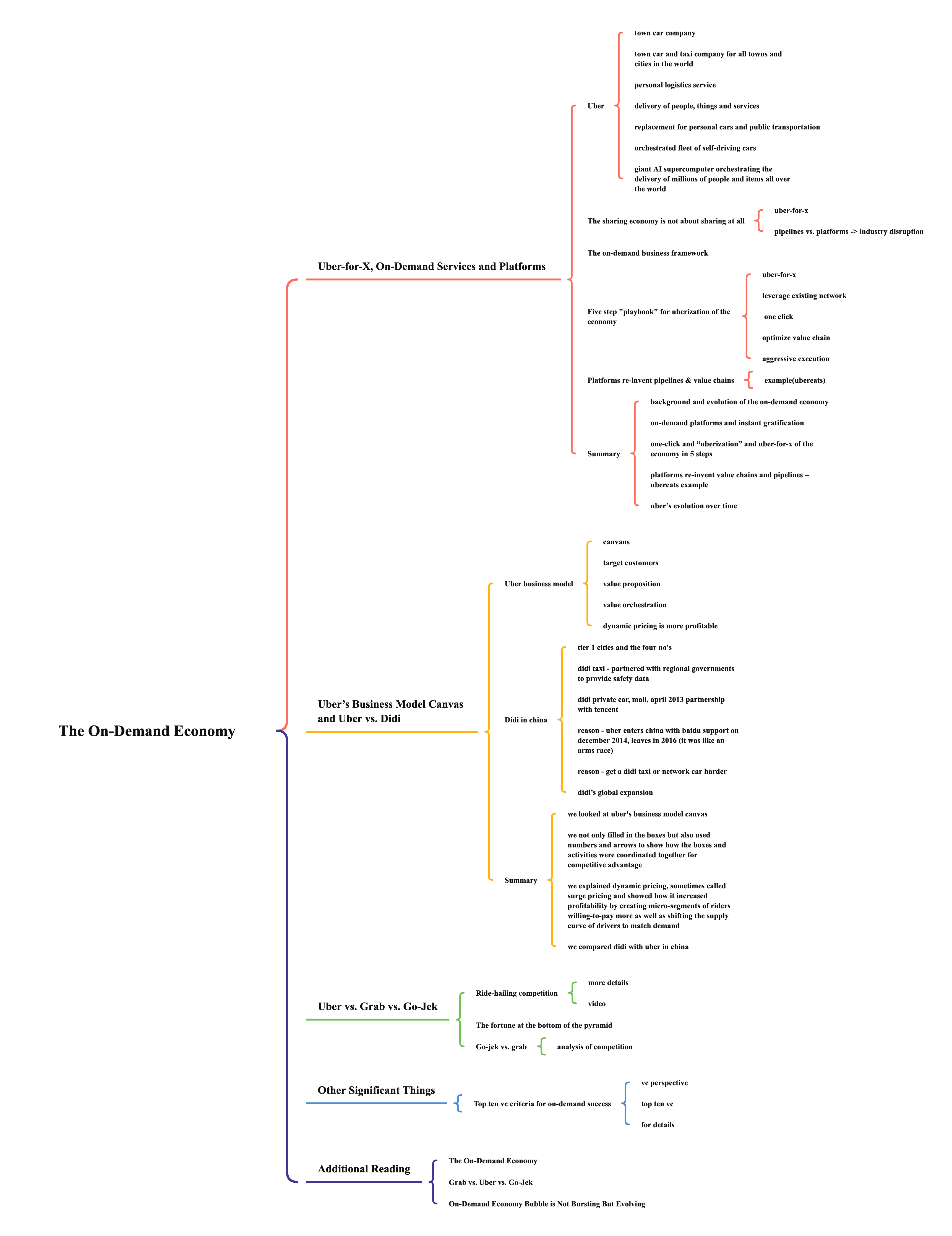
Uber-for-X, On-Demand Services and Platforms
- town car company
- town car and taxi company for all towns and cities in the world
- personal logistics service
- delivery of people, things and services
- replacement for personal cars and public transportation
- orchestrated fleet of self-driving cars
- giant AI supercomputer orchestrating the delivery of millions of people and items all over the world
The sharing economy is not about sharing at all
- uber-for-x
- for cars
- for buses
- for trucks
- for delivery trucks
- for scooters
- for e-scooters
- pipelines vs. platforms -> industry disruption

The on-demand business framework

Five step “playbook” for uberization of the economy
- uber-for-x
- leverage existing network
- one click
- optimize value chain
- aggressive execution
Platforms re-invent pipelines & value chains
- example (ubereats)
- order the food -> make the food -> put the food in the car -> deliver the food (from)
- make the food -> put the food in the car -> order the food -> deliver the food (to)
Summary
- background and evolution of the on-demand economy
- on-demand platforms and instant gratification
- one-click and “uberization” and uber-for-x of the economy in 5 steps
- platforms re-invent value chains and pipelines – ubereats example
- uber’s evolution over time
Uber’s Business Model Canvas and Uber vs. Didi
Uber business model
- canvas
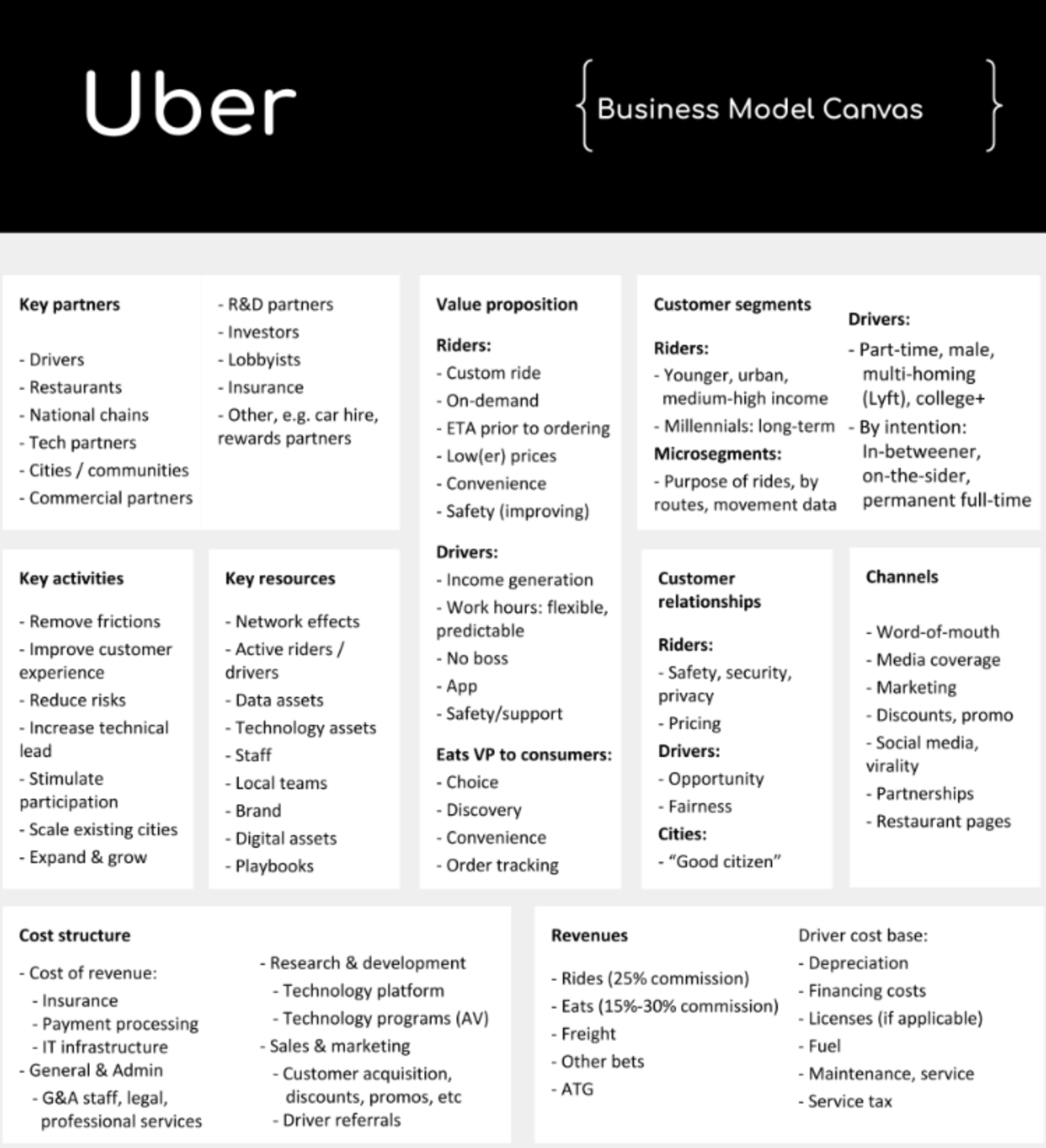
- target customers
- end users
- upper class
- business
- technology
- urban middle-class
- suppliers
- drivers
- end users
- value proposition
- value proposition for both sides
- end users
- secure, trustworthy and guaranteed ride with shorter waiting
- drivers
- busier and efficient days for drivers
- end users
- value proposition for both sides
- value orchestration
- mobile app instant services + no company cars + no employee-drivers
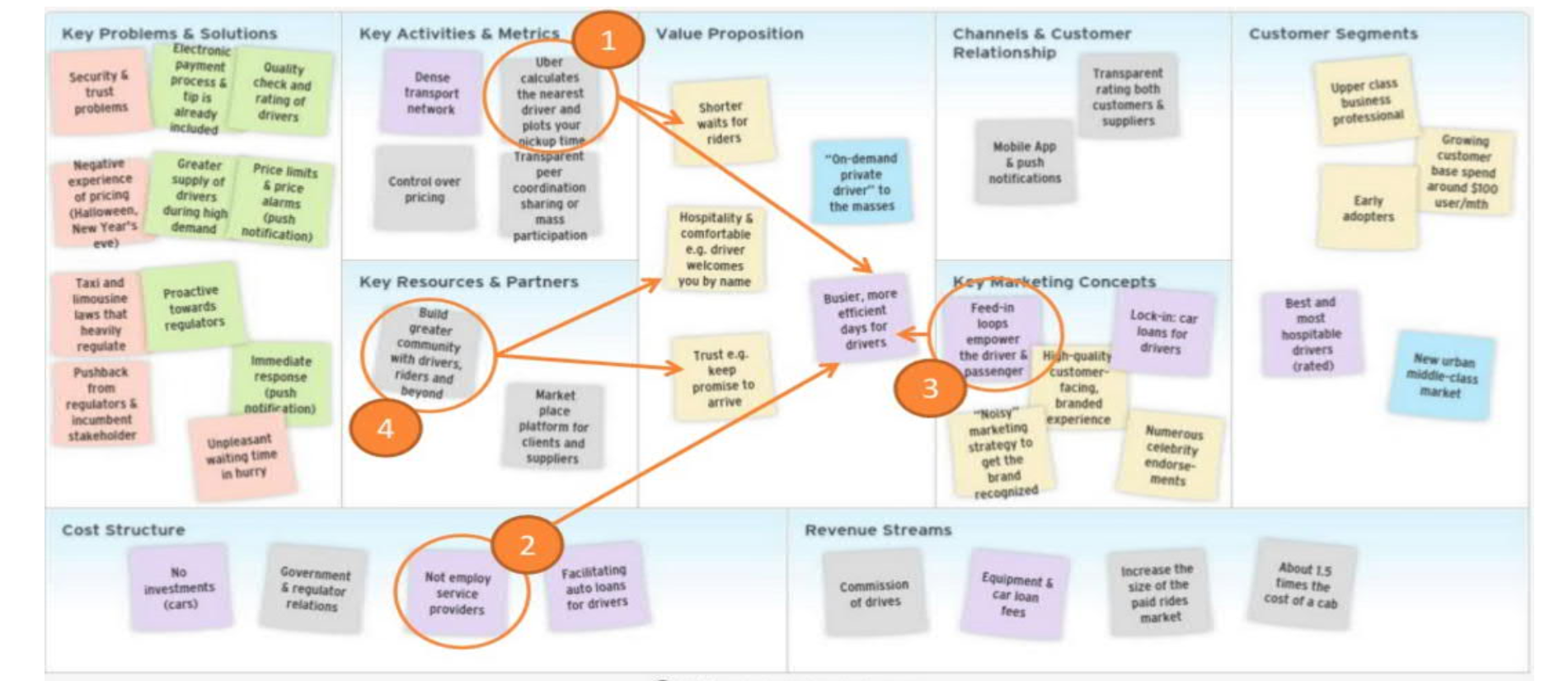
- dynamic pricing is more profitable
- for more details
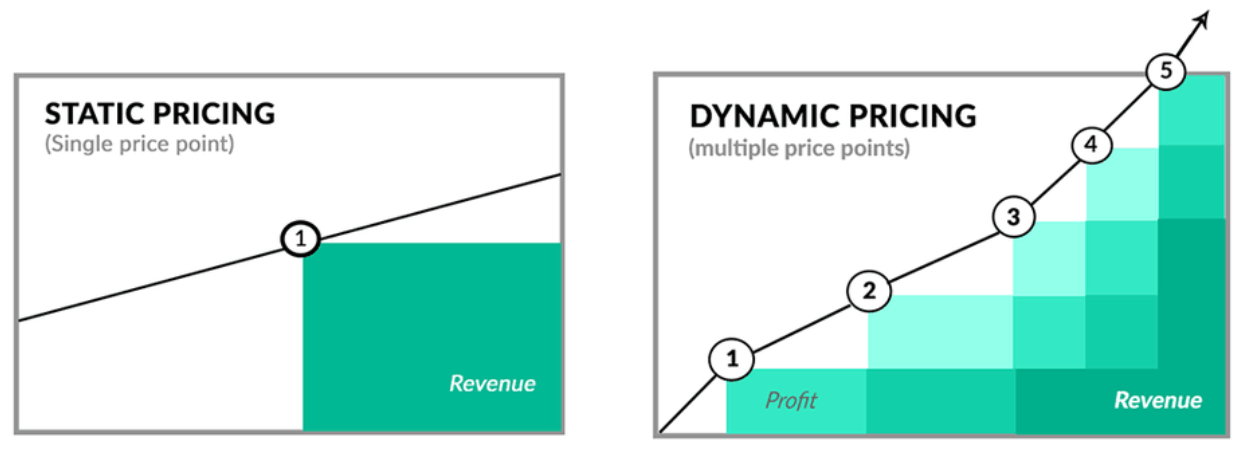
- for more details
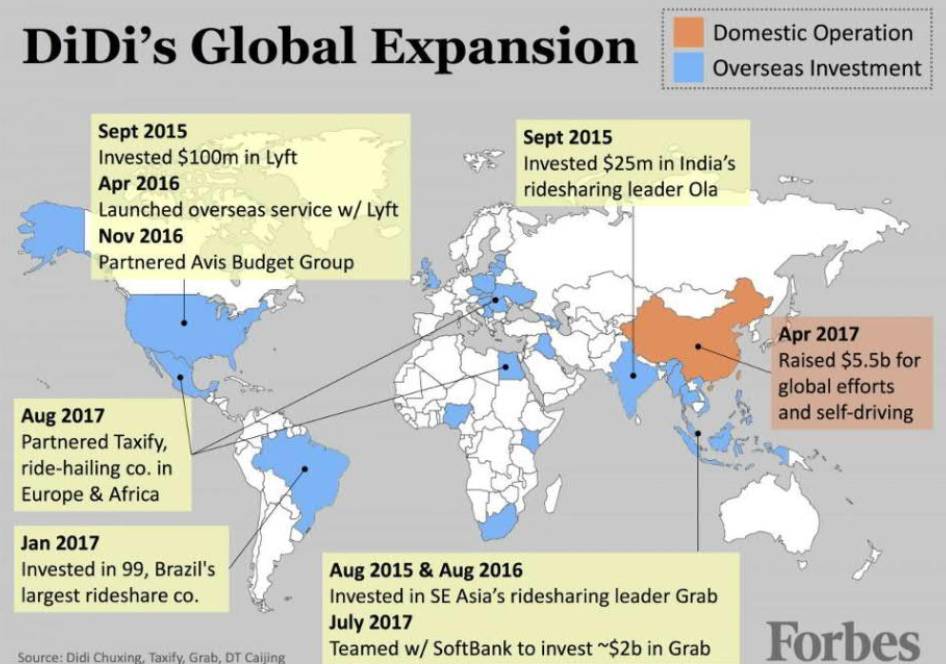
Didi in china
- tier 1 cities and the four no’s
- no unlicensed taxis
- no fare increases
- no mandatory membership
- no hardware
- didi taxi - partnered with regional governments to provide safety data
- didi private car, mall, april 2013 partnership with tencent
- reason - uber enters china with baidu support on december 2014, leaves in 2016 (it was like an arms race)
- didi invests $100m in september 2015 in lyft
- didi and uber burn $1B/year in subsidies to drivers and riders
- apple invest $1B in didi
- uber raises $3.5B from saudi arabia’s public investment fund
- reason - get a didi taxi or network car harder
- didi’s global expansion
Summary
- we looked at uber’s business model canvas
- we not only filled in the boxes but also used numbers and arrows to show how the boxes and activities were coordinated together for competitive advantage
- we explained dynamic pricing, sometimes called surge pricing and showed how it increased profitability by creating micro-segments of riders willing-to-pay more as well as shifting the supply curve of drivers to match demand
- we compared didi with uber in china
Uber vs. Grab vs. Go-Jek
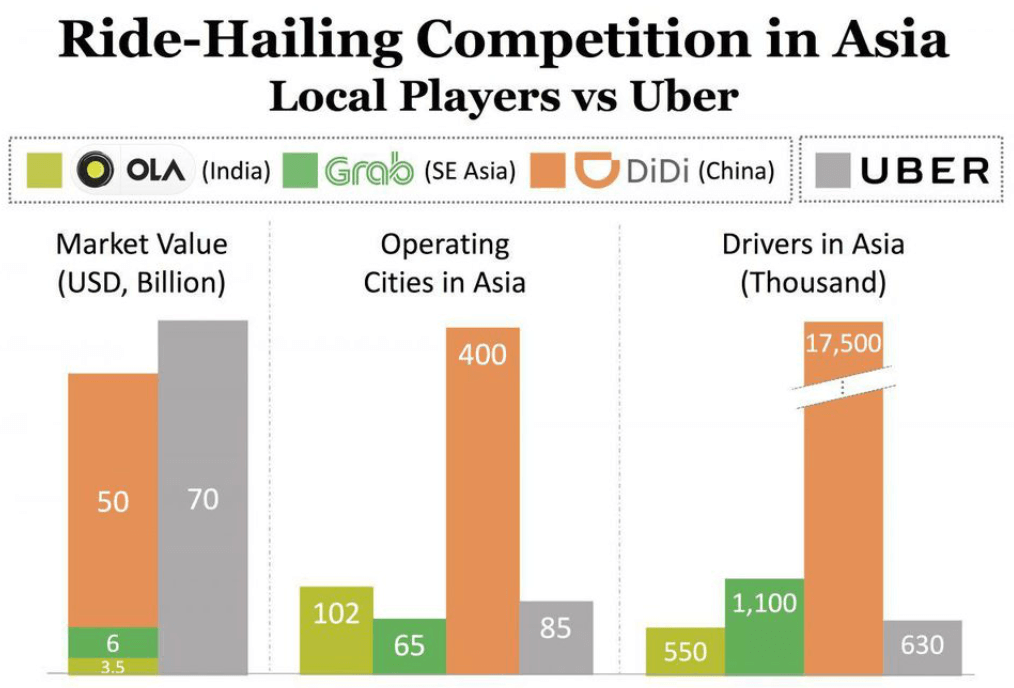
Ride-hailing competition
- more details
- video
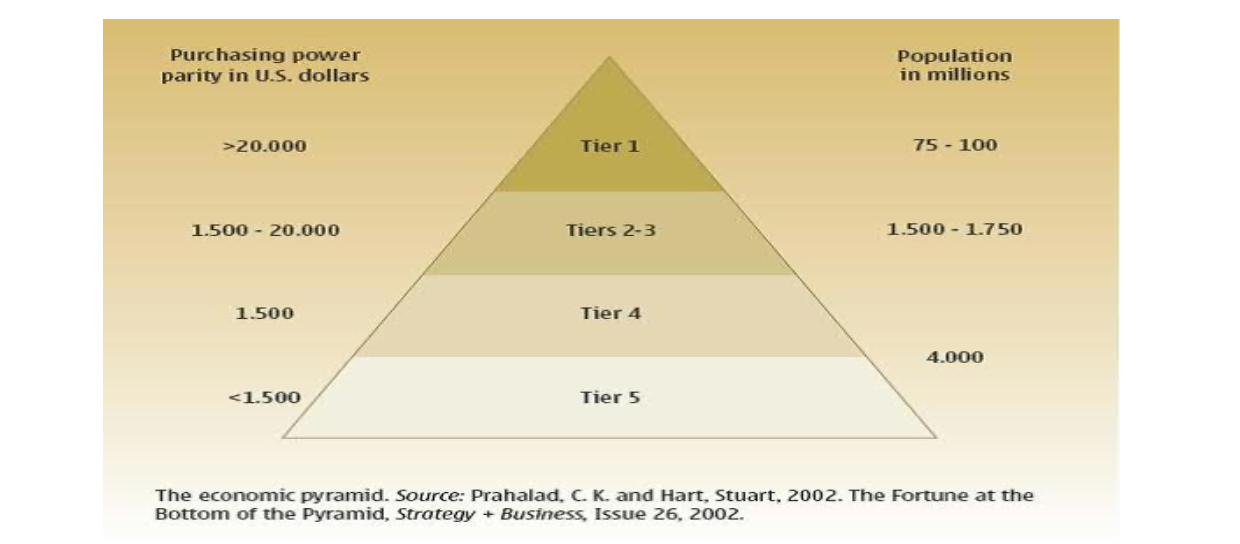
The fortune at the bottom of the pyramid
Go-jek vs. grab
- analysis of competition
Other Significant Things
Top ten vc criteria for on-demand success
- vc perspective
- frequency matters in mobile and helps build habitual behavior (more important)
- be careful of hidden unit costs and poor accounting (more important)
- look for technology leverage and economies of scale in the model (more important)
- be weary of simply becoming a more efficient agency
- be very careful of discount customers, can prop up short term growth, but not sustainable and can cause negative chain reactions that are hard to fix
- look for teams that are equal parts star operators and technologists
- top ten vc
- vision
- market size
- go-to-market
- unit economics
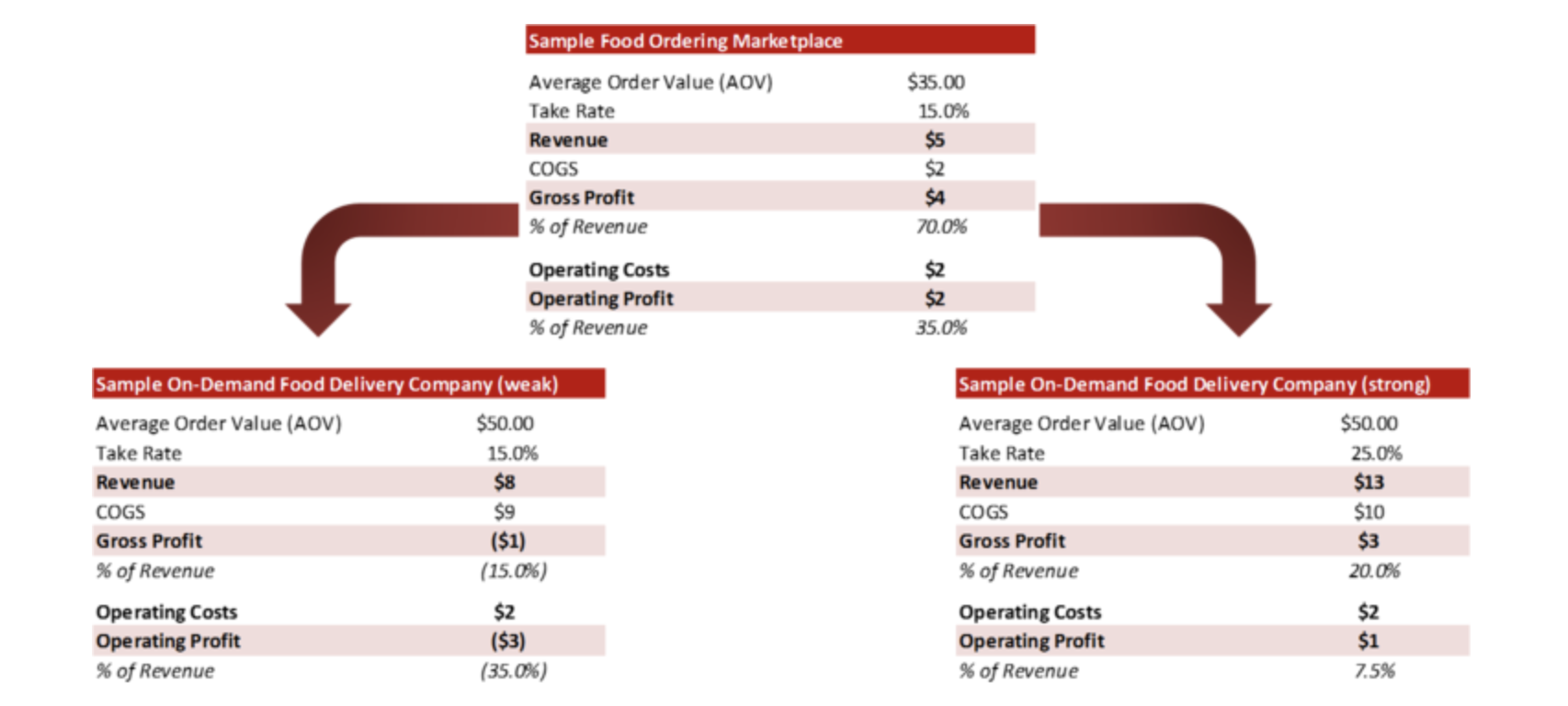
- retention and life time value (ltv)
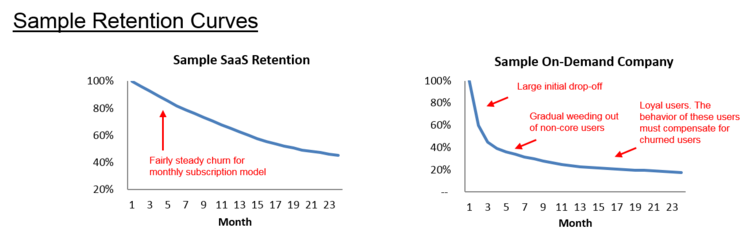
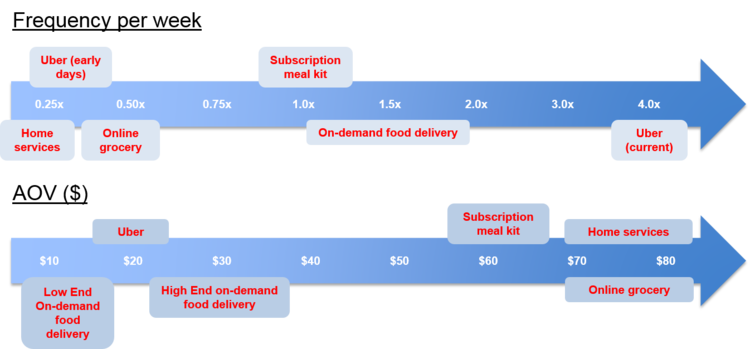
- supply side
- operational excellence
- market growth
- network effects
- technology leverage
- for details