3 minutes
ICOM6045 Web Security - More Examples
Man-In-The-Browser Attack
- schematic diagram
- medium
- the trojan works by utilizing prevalent tools/plugins to enhance browser capabilities
- Browser Helper Objects (BHO)
- extensions
- user scripts
- spam email
- virus downloaded from malicious website
- free software downloaded from malicious website or forum
- the trojan works by utilizing prevalent tools/plugins to enhance browser capabilities
- hard to detect by virus scanning software
- example - attack bank account to stole money
- infect your browser
- waiting for you to login to your Internet banking account
- redirect you to the “hacker’s” server
- capture your username/password and the one-time password (to login)
- pretend the one-time password is not correct and ask you to input the second one-time password (transfer money)
- crash the victim’s browser in order to have more time
- use 2 one-time passwords to transfer money to another account in another country
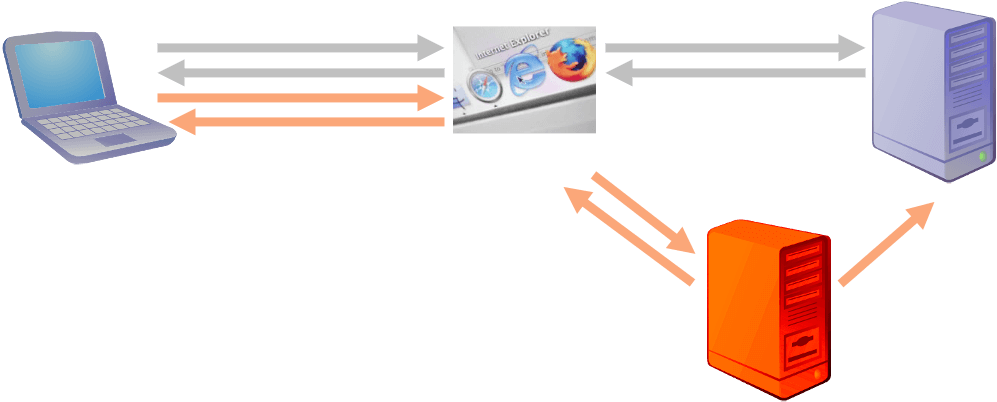
Cross Site Forgery Request (CSFR)
- threats from server to client
- general key idea
- after client authenticated to a server, the authentication info is stored in client (usually as cookie) (e.g. user login bank website)
- by attracting/cheating the user to click a malicious link, user will visit the hacker site, to let the hacker site do the following
- hacker site to create a ‘faked request’, and let the user to send the ‘faked request’ to the server, to carry out a ‘faked transaction’ (like money transfer)
- framework
CAPTCHA Case
- full name
- completely automated public turing test to tell computers and humans apart
- automatically generate challenges which intends to
- provide a problem easy enough for all humans to solve
- the problem cannot be solved by a computer program currently, unless it is specially designed to circumvent specific CAPTCHA systems
- e.g. a human user can read distorted text while bots cannot
- purposes
- is usually used to protect websites against bots which abuse the websites
- positions
- at a login form to prevent dictionary attack
- before account registration
- before showing an e-mail on a personal website to avoid spammers getting your e-mail address when they crawl the web to look for valid e-mail addresses
- implementations
- rely on visual perception (more than distorted text)
- identifying an object that does not belong in a particular set of objects
- locating the center of a distorted image
- identifying distorted shapes
- 3D CAPTCHA, etc
- provide an audio version of the CAPTCHA for accessibility reasons
- rely on visual perception (more than distorted text)
- human attack
- some companies will provide a plug-in for your program
- when you program sees a CAPTCHA request, the picture will send to the company, and the company will have a group of humans to “enter” the answer for you
Spyware - Tracking Cookies
- online advertising
- data collection using tracking cookies
- example
- first site
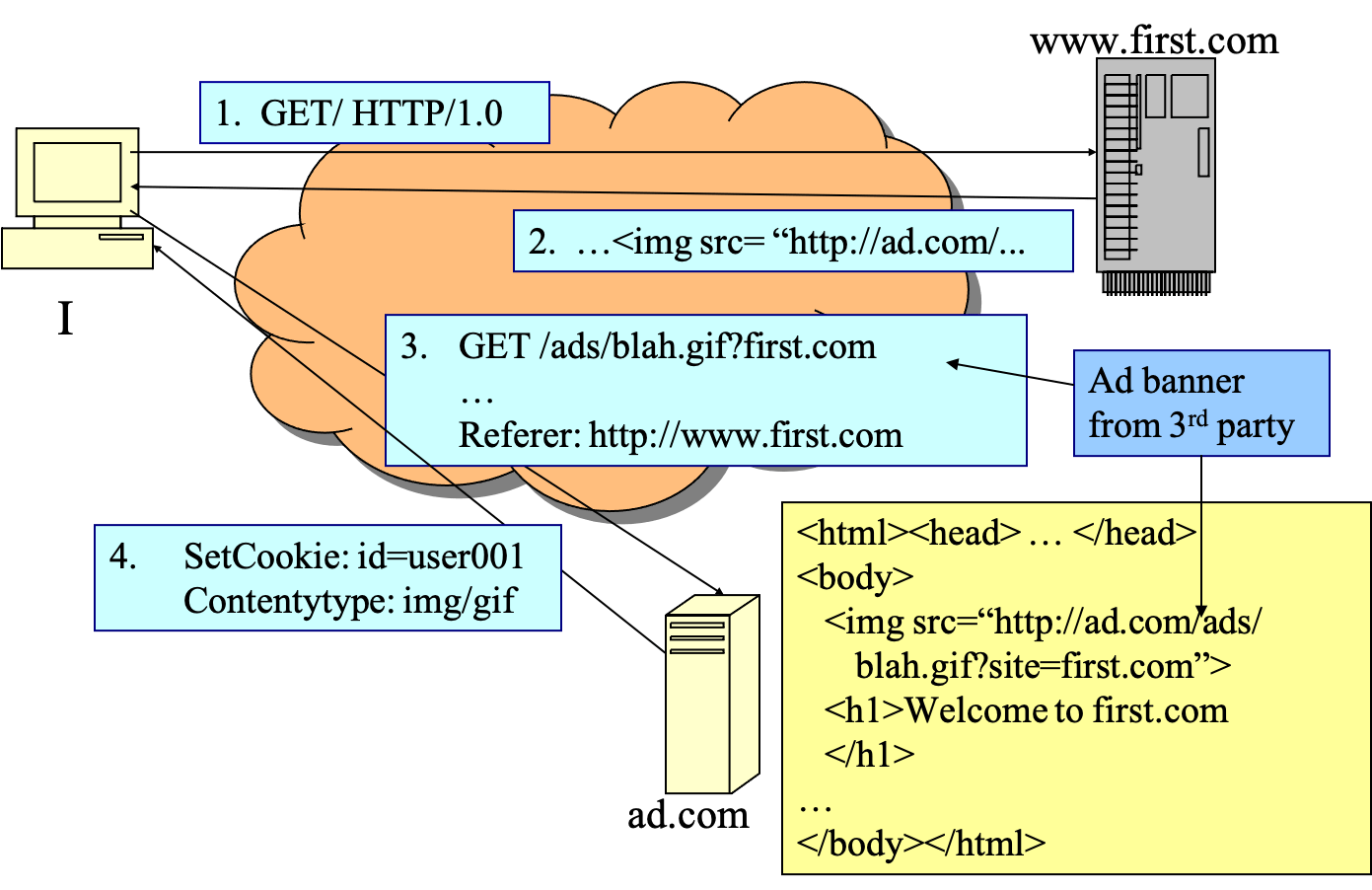
- second site
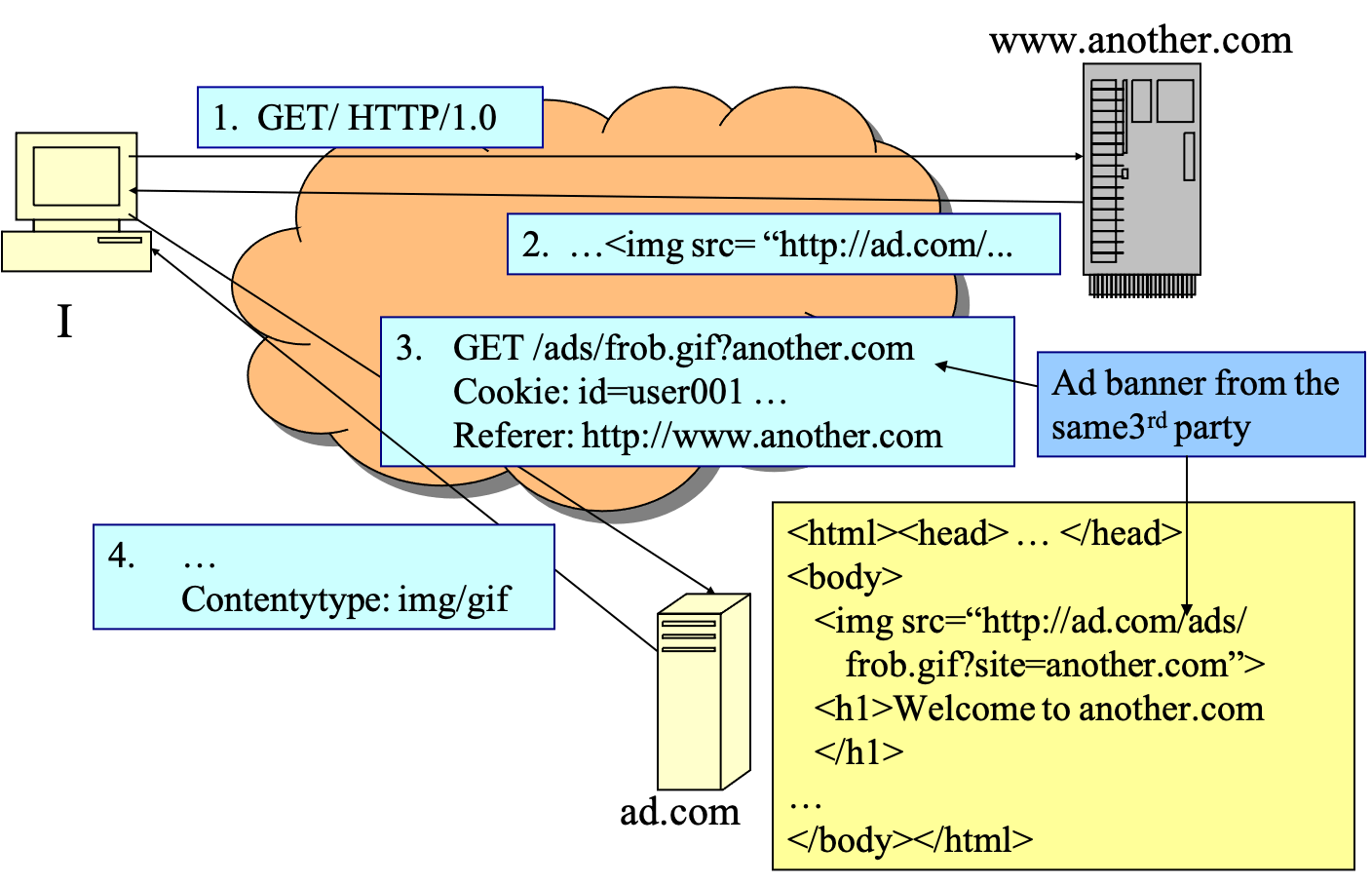
- first site
- ad.com know
- I have been to first.com and another.com
- the time I visit first.com and another.com
- other information: languages, character sets, ..
- IP addresses
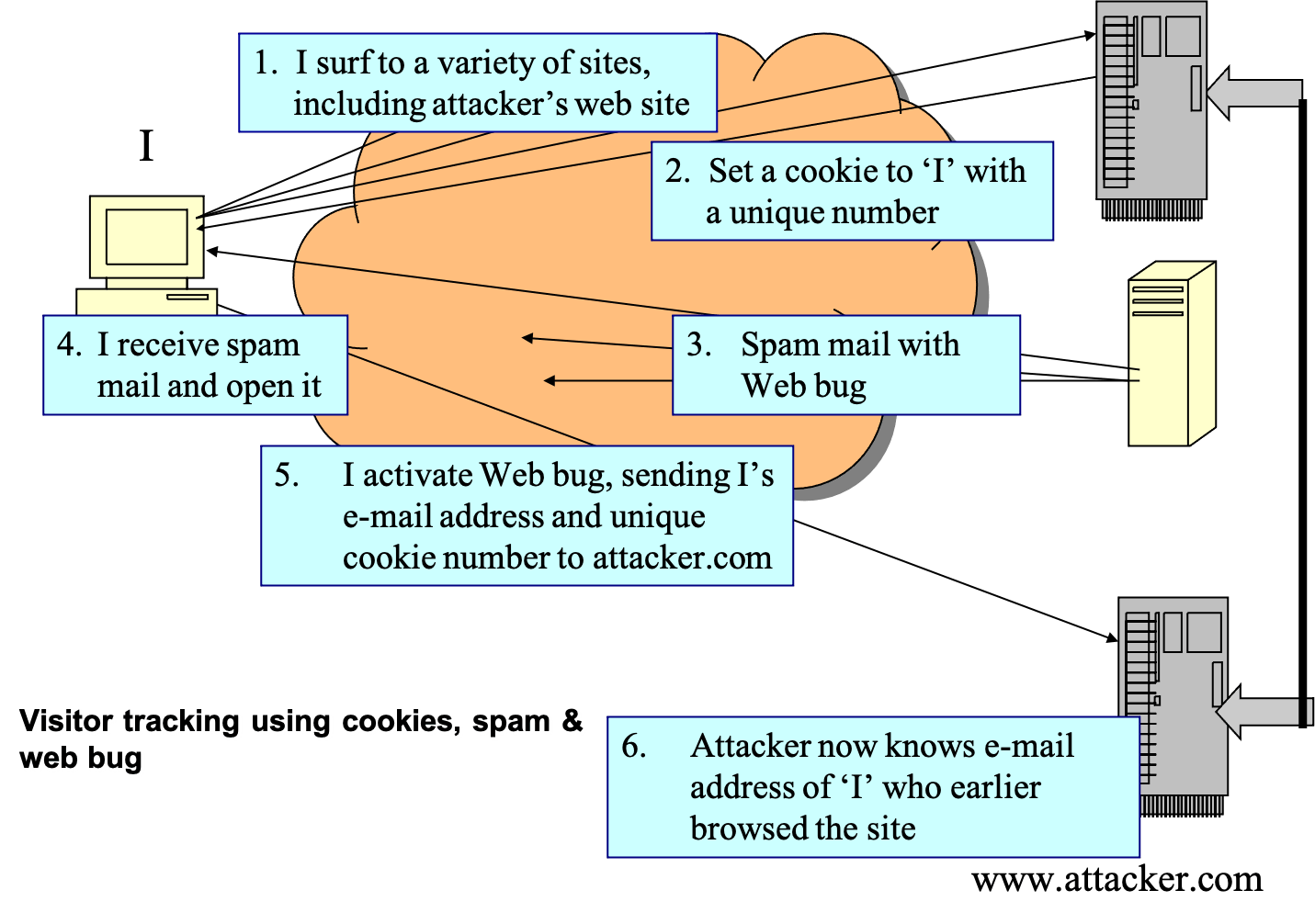
- visitor tracking
- tracking web site visitor using cookies, spam mail and web bug
- example
SQL Injection
- mechanism
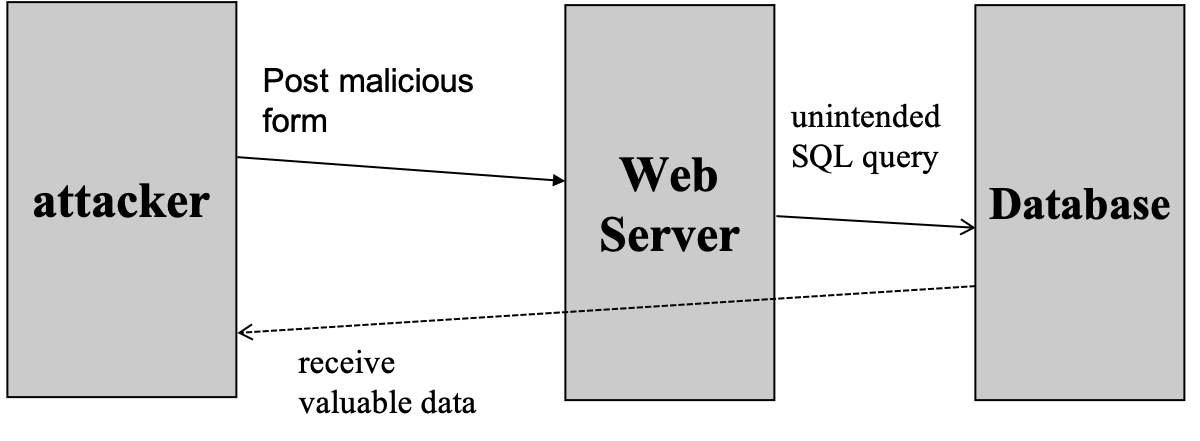
- example
- suppose user = “ ' or 1=1 – ” (URL encoded)
- then scripts does ok = execute(SELECT … WHERE user= ' ' or 1=1 – …)
- the “–” causes rest of line to be ignored
- now ok.EOF is always false and login succeeds
- the bad news
- easy login to many sites this way

- easy login to many sites this way
- key problem
- no input check, just like heartbleed
Cross Site Scripting (CSS)
- definition
- security defect in a web-based application that allows user data (e.g. cookies) to be disclosed to a malicious third party
- “cross-site” means the cookie is transferred from a client computer accessing a valid, but vulnerable, web-server site to the attacker’s site
- popular languages that create cross-site scripting problem: scripting languages or technologies that are used to build a web site
- security defect in a web-based application that allows user data (e.g. cookies) to be disclosed to a malicious third party
- session hijacking
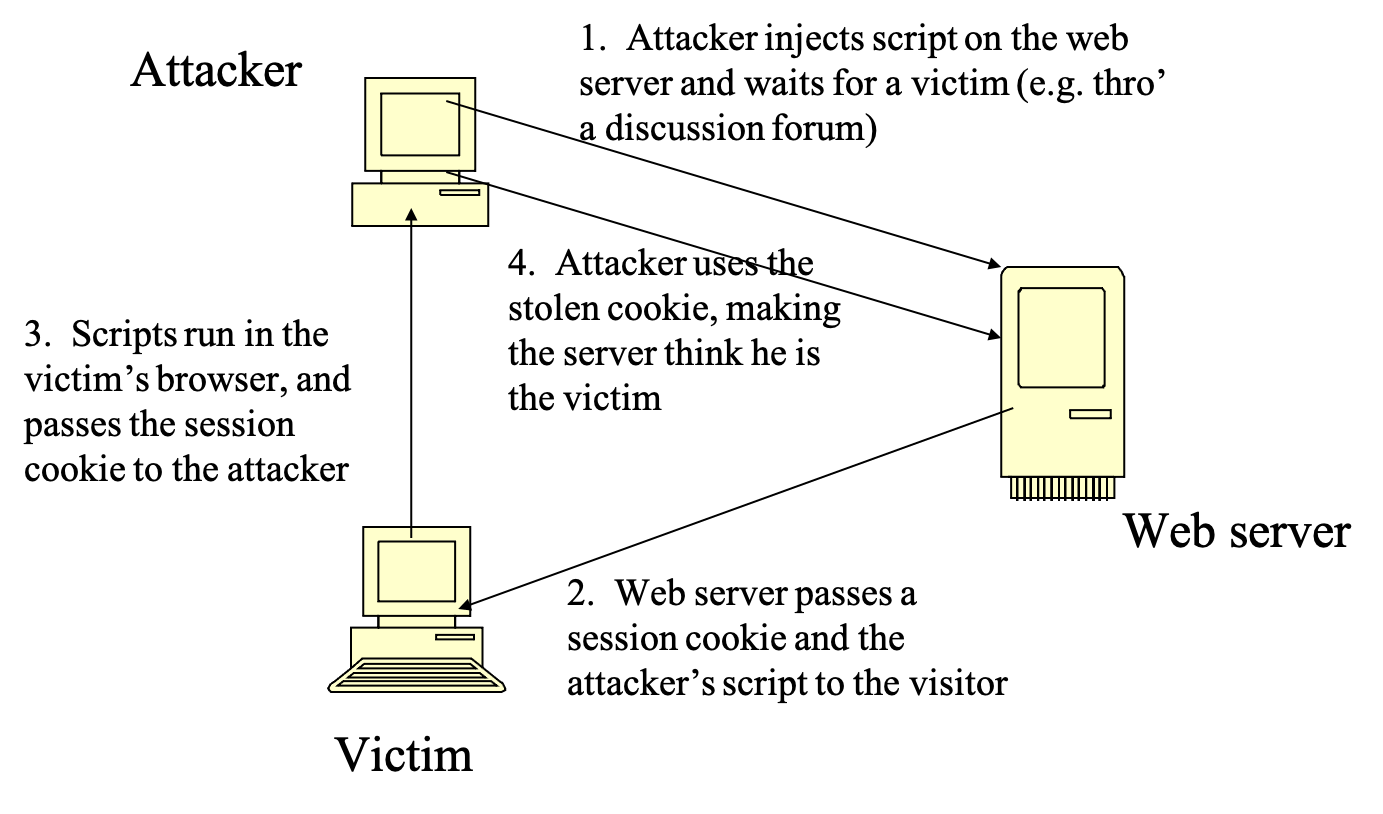
- attack string
- simple test string
<script>alert(“XSS”);</script> show an alert <script>alert(document.cookie);</script> show the user’s cookie- insert attack string
‘> <script>alert(“XSS”);</script> close out the quote of another tag- more complex attack string
';alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//\';alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//";alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//\";alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//--></SCRIPT>">'><SCRIPT>alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))</SCRIPT> '';!--"<XSS>=&{()} <IMG SRC="javascript:alert('XSS');"> - key problem
- no input check
icom6045 fundamentals of e-commerce security web security examples case study
631 Words
2020-12-05 19:58