3 minutes
ECOM6013 Emerging and Disruptive Technologies, IoT and AI
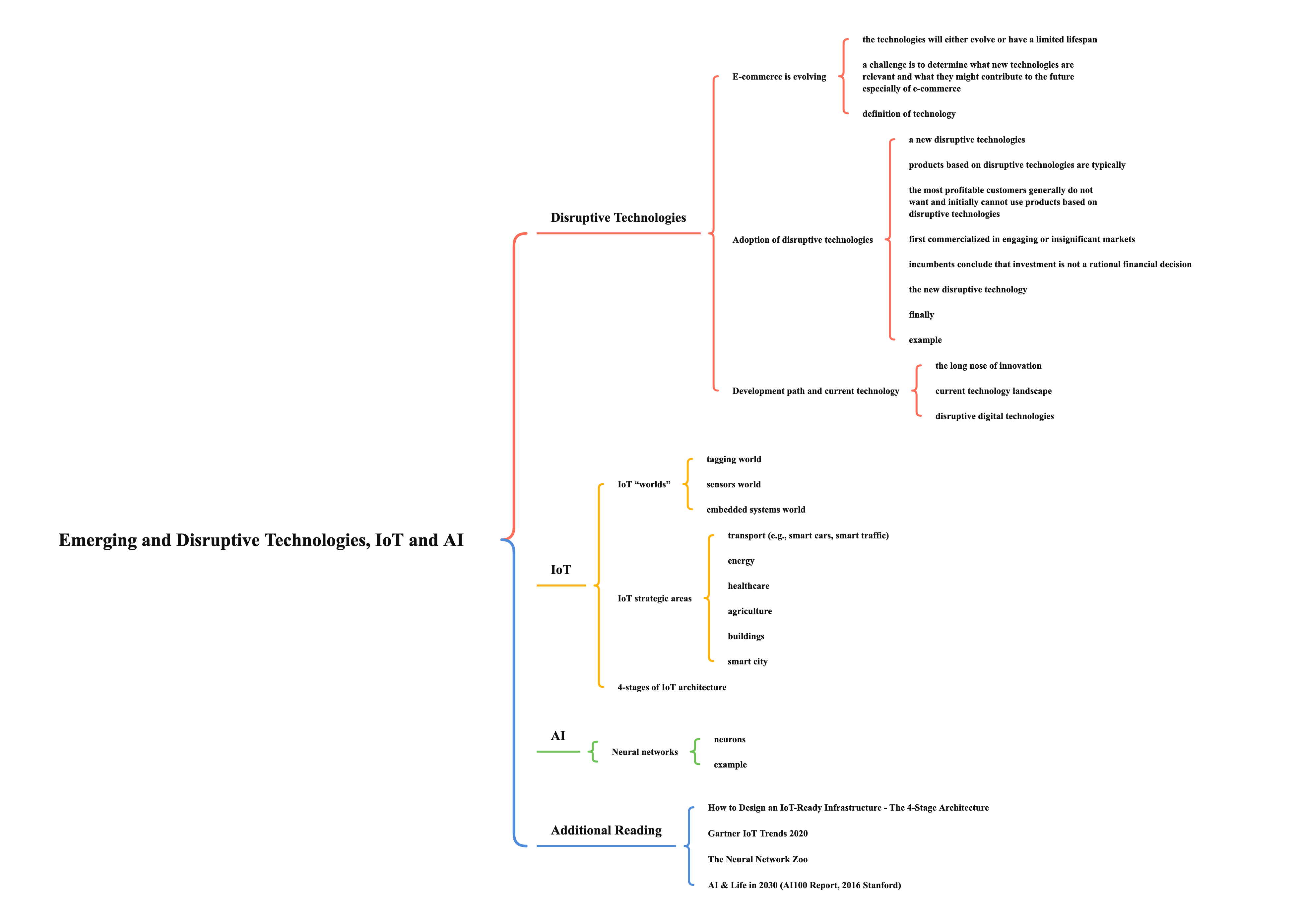
Disruptive Technologies
E-commerce is evolving
- the technologies will either evolve or have a limited lifespan
- a challenge is to determine what new technologies are relevant and what they might contribute to the future especially of e-commerce
- definition of technology
- the application of science, math, engineering, art, and other fields of knowledge to create tools and implementations deemed useful by a society
Adoption of disruptive technologies
- a new disruptive technology
- initially underperforms the dominant one along the dimensions mainstream customers in major markets have historically valued
- has other features a few fringe (and generally new) customers value
- products based on disruptive technologies are typically
- cheaper
- simpler
- smaller
- more convenient than those established on the dominant technology
- the most profitable customers generally do not want and initially cannot use products based on disruptive technologies
- first commercialized in engaging or insignificant markets
- incumbents conclude that investment is not a rational financial decision
- the new disruptive technology
- steadily improves in performance
- until it meets the standards of performance demanded by the mainstream market
- finally
- the new technology displaces the dominant one
- the new entrant displaces the dominant one in the mainstream market
- example
- Barnes & Noble (1873) (MC: $0.475B) vs Amazon (1995) (MC: $878B) - only 0.06%

- Barnes & Noble (1873) (MC: $0.475B) vs Amazon (1995) (MC: $878B) - only 0.06%
Development path and current technology
- the long nose of innovation
- the bulk of innovation is low-amplitude and takes place over a long period
- technologists should focus on refining existing technologies as much as on creation new ones
- therefore, most technology likely to have an impact in the next five years is already at least 15 years old and unrecognized
- examples: IoT and AI

- current technology landscape
- internet connecting the whole world at low cost
- cheap, small, dense data storage – hence big data possible
- high speed networks; ubiquitous WiFi and mobile network
- access to almost unlimited processing power at low cost
- Moore’s law leads to cheap, small processors and sensors
- embedded systems
- smart devices
- advancements in energy efficiency – yet more innovation needed
- a good example of disruptive technology is Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- disruptive digital technologies
- technologies which offer opportunities for business for new products and services for customers and can transform internal business processes
- a technology that changes the bases of competition by changing the performance metrics along which firms compete
- technology based on customer needs that drive customers to seek certain benefits in the products they use and form the basis for customer choices between competing products
- for IoT, we have the capability to fully connect and integrate a wide diversity of devices and objects into the online environment and interact with them
- for AI, we have Big Data and powerful cloud processing power to support it
IoT
IoT “worlds”
- tagging world
- is about identifying things
- identifiers such as RFIDs are attached to things (e.g., packages) to enable their automatic identification and tracking
- based on ID, the information about things can be accessed from a database or from the web
- sensors world
- is about sensing things
- “second hand” access to the properties of things, that can be perceived from the outside using a variety of available sensors
- embedded systems world
- is about reading things
- “first-hand” access to data possessed by things
- e.g., industrial machines or home electronics, already embedded with some processing and data storage capabilities
IoT strategic areas
- transport (e.g., smart cars, smart traffic)
- energy
- healthcare
- agriculture
- buildings
- smart city
4-stages of IoT architecture

AI
Neural networks
- neurons

- example
