6 minutes
ECOM6013 Internet and E-Commerce Security

Overview
Good e-commerce security
- to achieve highest degree of security, one needs
- new technologies
- organizational policies and procedures
- industry standards and government laws

- other factors
- cost of security versus potential loss
- security often breaks at weakest link
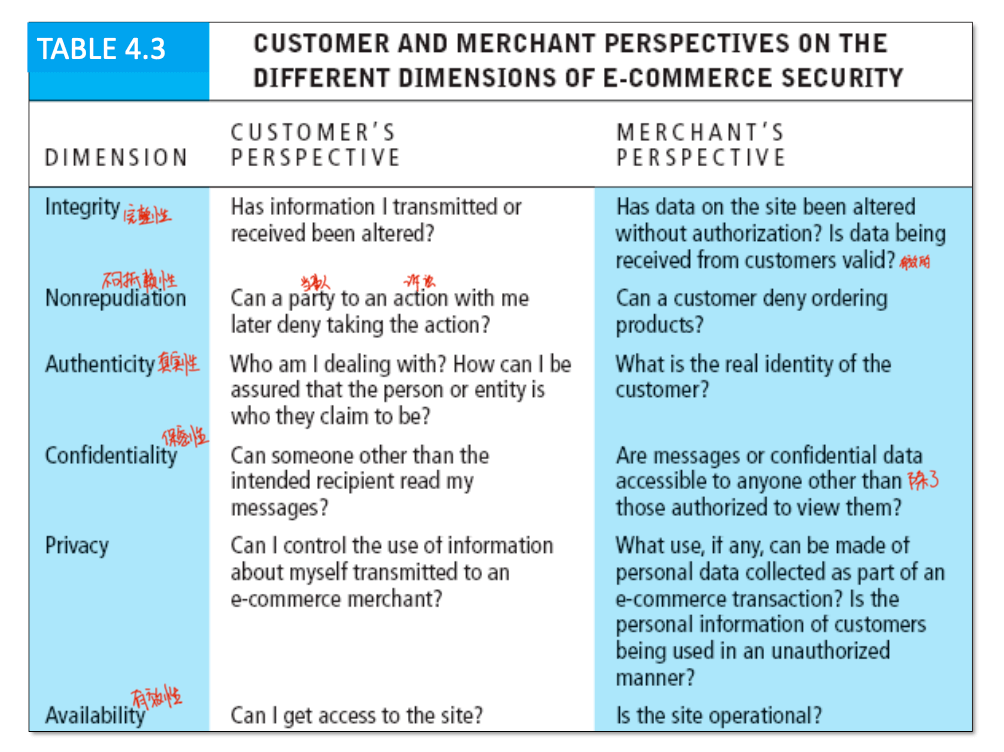
Different perspectives between customers and merchants
Basic E-Commerce Security
The tension between security and other values
- security vs ease of use
- the more security measures added, the more difficult a site is to use, and the slower it becomes
- security vs desire of individuals to act anonymously
- use of technology by criminals to plan crimes or threaten nation-state
Basic security issues and landscape
- e-commerce security requirements (4A + N)
- authentication
- authorization
- auditing
- availability
- nonrepudiation
- risk
- the probability that a vulnerability will be known and used
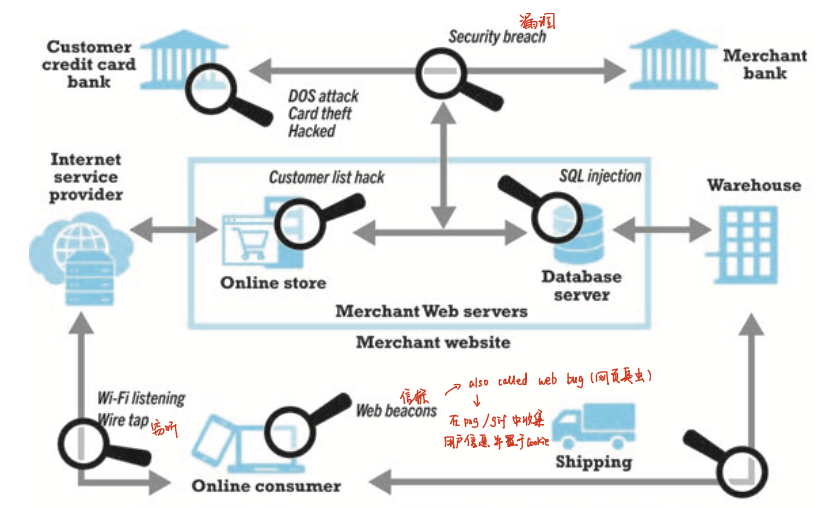
- 3 key points of vulnerability
- client
- server
- communication pipeline (network channels)
- social engineering
- a type of nontechnical attack that uses some plan or stories to trick users into revealing information or performing an action that compromises a computer or network
- spam
- the electronic equivalent of junk mail or calls
Threats and solutions for the e-commerce today
- threats
- money thefts
- identity thefts
- malware
- solutions
- authentication
- intrusion checking
- firewalls
- education
- scenario in e-commerce transaction
- most common security examples
- malicious code
- viruses
- worms
- ransomeware
- trojan horses
- backdoors
- bots, botnets
- unwanted programs
- browser parasites
- monitor and change user’s browser
- adware
- used to call pop-up ads
- spyware
- tracks user’s keystrokes, emails, instant message
- browser parasites
- phishing
- deceptive online attempt to obtain confidential information
- social engineering, e-mail scams, spoofing legitimate web sites
- used for identity fraud and theft
- hacking and cybervandalism
- hackers vs crackers
- cybervandalism: intentionally disrupting, defacing, destroying web site
- hacktivism
- data breach
- organization loses control over corporate information to outsiders
- leading causes
- hacking
- unauthorized access
- employee error/negligence
- credit card fraud/theft
- fear of stolen credit card information deters online purchases
- hackers target corporate servers; use data to establish credit under false identity
- online companies at higher risk than offline
- spoofing: misrepresenting self by using fake e-mail address
- pharming: spoofing a web site
- redirecting a URL to a new, fake web site
- spam/junk websites
- offer collection of advertisements for other sites, which may contain malicious code
- denial of service (DoS) attack
- hackers flood site with useless traffic to overwhelm network
- distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack
- hackers use multiple computers to attack target network
- sniffing
- eavesdropping program that monitors information traveling over a network (to get to “weak spots”)
- insider jobs
- single largest financial threat
- poorly designed security policy and server/client software
- social network issues
- social networks an environment for
- viruses, site takeovers, identity fraud, malware-loaded apps, click hijacking, phishing, spam
- manual sharing scams
- sharing of files that link to malicious sites
- fake offerings, fake like buttons, and fake apps
- social networks an environment for
- mobile platform issues
- little public awareness of mobile device vulnerabilities
- cloud security issues
- DDoS attacks
- infrastructure scanning
- lower-tech phishing attacks yield passwords and access
- use of cloud storage to connect linked accounts
- lack of encryption and strong security procedures
- IoT security issues
- challenging environment to protect
- vast quantity of interconnected links
- near identical devices with long service lives
- many devices have no upgrade features
- little visibility into workings, data, or security
- malicious code
Assurance model and defense objectives
- CIA security triad
- confidentiality
- integrity
- availability
- technology solutions
- protecting internet communications
- cryptography
- securing channels of communication
- SSL, TLS, VPNs, Wi-Fi
- protecting networks
- firewalls, proxy servers, IDS
- protecting servers and clients
- OS security, anti-virus software
- protecting internet communications
- basic concept of user authentication
- something you know
- password, PIN, “motherʼs maiden name”, OTP
- something you have
- physical key, token, magnetic card, smartcard
- something you are
- fingerprint, voice, retina, iris
- best to use two or three of the above, that is why we now have 2 factors authentication (2FA)
- something you know
- encryption
- transforms data into cipher text readable only by sender and receiver
- secures stored information and information transmission
- provides 4 of 6 key dimensions of e-commerce security
- authentication
- confidentiality
- message integrity
- nonrepudiation
- types
- symmetric key cryptography
- sender and receiver use same digital key to encrypt and decrypt message
- requires different set of keys for each transaction
- strength of encryption
- length of binary key used to encrypt data
- data encryption standard (DES, 1977)
- triple DES encryption algorithm, 56-bit encryption key, 64 bits/block
- advanced encryption standard (AES, 2000)
- most widely used symmetric key algorithm
- uses 128-, 192-, and 256-bit encryption keys, 128-bits/block
- other standards use keys with up to 2,048 bits
- public key encryption
- uses two mathematically related digital keys
- public key (widely disseminated)
- private key (kept secret by owner)
- both keys used to encrypt and decrypt message
- once key used to encrypt message, same key cannot be used to decrypt message
- sender uses recipient’s public key to encrypt message
- recipient uses his/her private key to decrypt it
- uses two mathematically related digital keys
- symmetric key cryptography
- usage
- public key encryption using digital signature and hash digests
- hash function
- mathematical algorithm (e.g. MD5 and SHA-1) that produces fixed-length number called message or hash digest
- sender applies hash function to the message and then encrypts the message and the hash digest with recipient’s public key
- sender then encrypts the whole package with sender’s private key — creating digital signature — for authenticity, nonrepudiation
- recipient first uses sender’s public key to authenticate the message and then the recipient’s private key to decrypt the hash digest and the message
- hash function
- digital envelopes
- addresses weaknesses of
- public key encryption
- computationally slow, decreased transmission speed, increased processing time
- symmetric key encryption
- insecure transmission lines
- public key encryption
- uses symmetric key encryption to encrypt document (much more efficient computationally)
- uses public key encryption to encrypt and send symmetric key
- addresses weaknesses of
- public key encryption using digital signature and hash digests
- limits
- does not protect storage of private key
- PKI not effective against insiders, employees
- protection of private keys by individuals may be haphazard
- no guarantee that verifying computer of merchant is secure
- CAs are unregulated, self-selecting organizations
- does not protect storage of private key
- digital certificates and PKI
- digital certificate includes
- name of subject/company
- subject’s public key
- digital certificate serial number
- expiration date, issuance date
- digital signature of certification authority (trusted third party institution) that issues certificate
- PKI
- CAs and digital certificate procedures that are accepted by all parties
- digital certificate includes
- securing channles of communication
- SSL/TLS
- establishes a secure, negotiated client-server session in which URL of requested document, along with contents, is encrypted
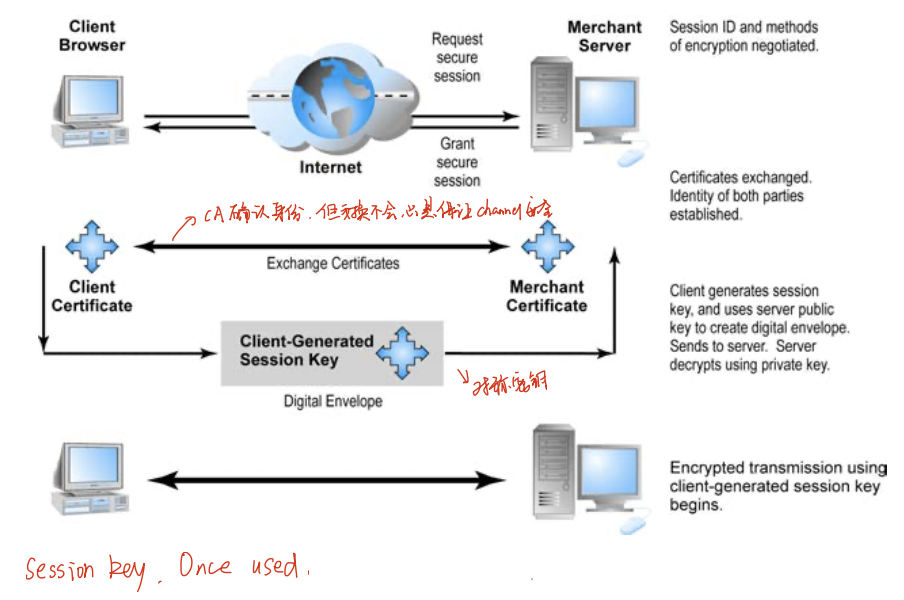
- establishes a secure, negotiated client-server session in which URL of requested document, along with contents, is encrypted
- S-HTTP
- provides a secure message-oriented communications protocol designed for use in conjunction with HTTP
- virtual private network (VPN)
- allows remote users to securely access internal network via the internet, using point-to-point tunneling protocol (PPTP)
- SSL/TLS
- protecting networks
- firewall
- hardware or software that filters packets
- prevents some packets from entering the network based on security policy
- 2 main methods
- packet filters
- application gateways
- proxy servers (proxies)
- software servers that handle all communications originating from or being sent to the internet
- firewall
- protecting servers and clients
- operating system security enhancements
- upgrades, patches
- anti-virus software
- easiest and least expensive way to prevent threats to system integrity
- requires daily updates
- operating system security enhancements
- managing risk includes
- technology
- effective management policies
- public laws and active enforcement
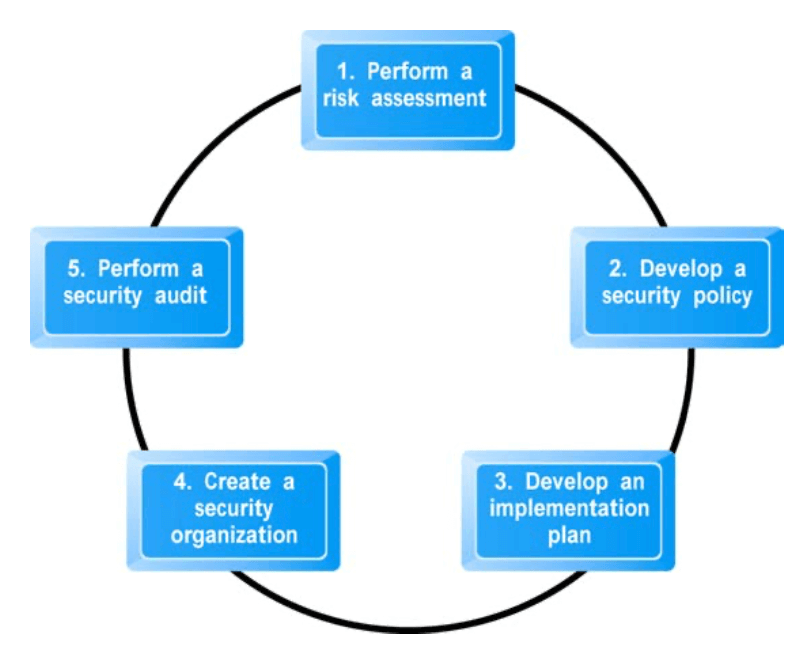
- a security plan: management policies
- risk assessment
- security policy
- implementation plan
- security organization
- access controls
- authentication procedures, including biometrics
- authorization policies, authorization management systems
- security audit