3 minutes
ECOM6013 Introduction to E-Commerce Technology
E-Commerce and Data Science
E-commerce is largely and exercise in understanding the clients
- containing their capabilities, desires, etc.
- matching clients with technologies and goals
- exploring scalability
- chanllenges of new markets
E-Commerce vs E-Business
E-commerce
- definition
- usually
- use of internet and/or web to transact business
- generally
- refer to any networked commerce activity
- formally
- digitally enabled commercial transactions between and among organizations and individuals
- usually
- traditional e-commerce
- features
- passive consumer
- sales-force driven
- fixed prices
- information asymmetry
- features
- current e-commerce
- reason of importance
- e-commerce technology is different, more powerful than previous technologies
- e-commerce bringing fundamental changes to commerce
- features
- ubiquity
- global reach
- universal standards
- information richness
- interactivity
- information density
- personalization/customization
- social technology
- trends
- new business models based on social technologies, consumer-generated content, and services (e.g., innovative payment systems)
- broadband and wireless access continue to grow
- mobile e-commerce is booming
- traditional media losing subscribers
- e-commerce has traditionally been early adopters (and influencers) of new technologies
- local-based, augmented reality (AR) and AI technologies & applications now beginning to mature
- types
- classified by market relationship
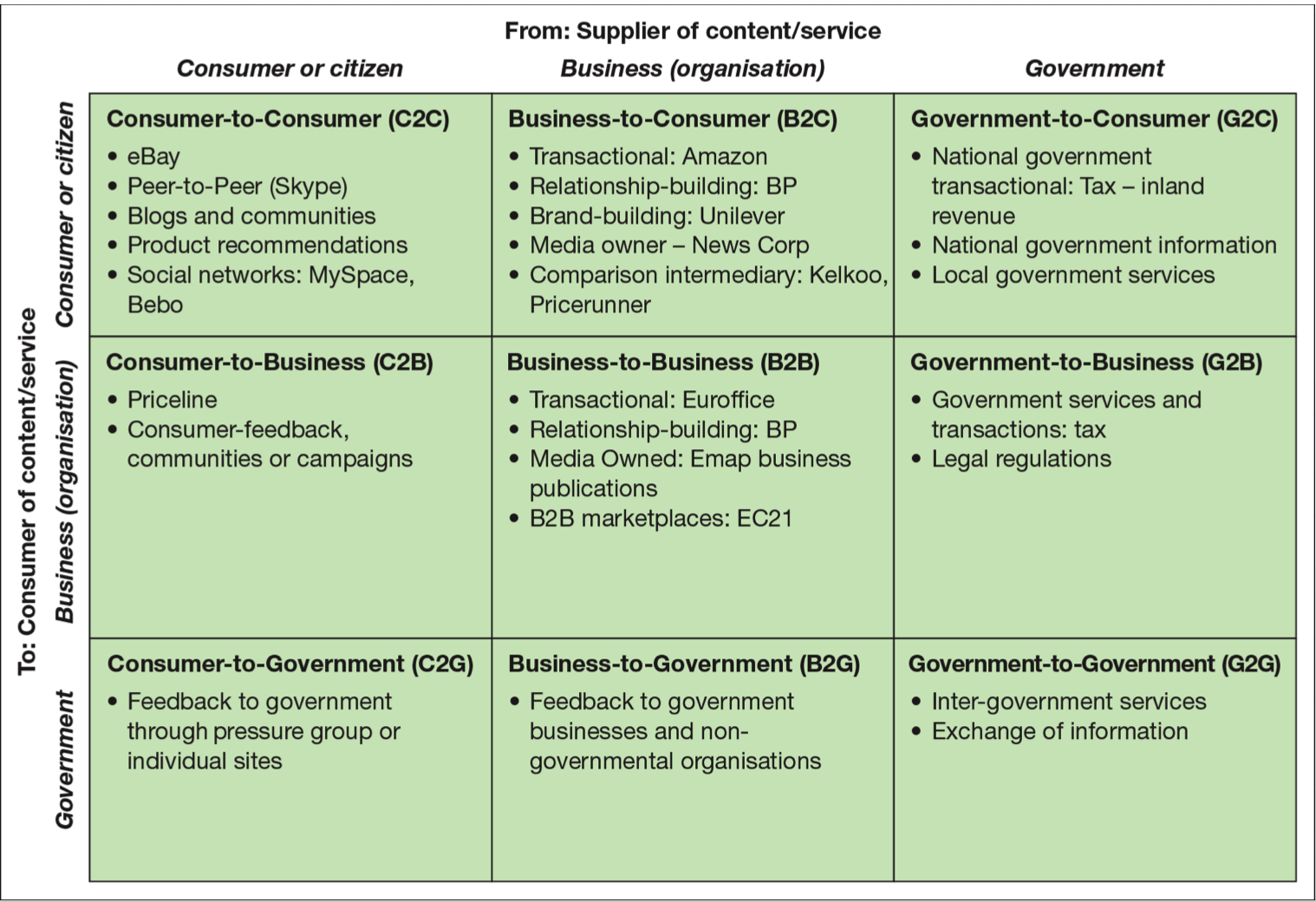
- classified by technology used
- peer-to-peer (P2P)
- mobile commerce (m-commerce)
- online-to-offline (O2O)
- classified by market relationship
- reason of importance
- organizing themes and trends
- technology
- development and mastery of digital computing and communications technology
- mobile platform has made mobile e-commerce reality and affordable smartphones plus 5G will make more impact
- business
- new technologies present businesses with new ways of organizing production and transacting business
- all forms of e-commerce show very strong growth and Covid-19 amplifies this
- society
- intellectual property, individual privacy, public welfare policy
- increased online social interaction and sharing, but we begin to see the negative impacts of social media
- technology
- relevant academic disciplines
- technical approach
- computer science
- management science
- information systems
- electrical & electronic engineering
- behavioral approach
- information systems
- economics
- marketing
- management
- finance/accounting
- sociology
- technical approach
E-business
- digital enablement of transactions and processes within a firm, involving information systems under firm’s control
- does not include commercial transactions involving an exchange of value across organizational boundaries
Potential Limitations and Predictions for the Future
Potential limitations on the growth of B2C e-commerce
- expensive technology
- sophisticated skill set
- persistent cultural attraction of physical markets and traditional shopping experiences
- persistent global inequality limiting access to telephones and computers
- saturation and ceiling effects
- de-globalization and trade war
Predictions/questions/challenges for the future
- technology will propagate through all commercial activity
- prices will rise to cover the real cost of doing business
- e-commerce margins and profits will rise to levels more typical of all retailers
- cast of players will change
- traditional fortune 500 companies will play dominant role
- new startup ventures will emerge with new products, services
- number of successful pure online stores will remain smaller than integrated offline/online stores
- growth of regulatory activity worldwide
- influence of cost of energy